The concept of a hybrid energy system is relatively simple…
Two forms of alternative energy combined to create a sustainable and environmentally sound system. A hybrid energy system most often consists of two or more renewable energy sources that provide greater efficiency and balance in terms of clean energy supply. Not all forms of clean energy are compatible with one another, so the field of prevalence of hybrid energy systems is somewhat limited. The most common combinations seen in this field are wind and solar energies. Solar has been cited for its potential in making hydrogen fuel cells more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Comparing Hybrid Energy Systems and Microgrids: Emphasizing Similarities
Hybrid energy systems and microgrids are closely related in their goals and methods, aiming to provide sustainable, reliable energy through integrated, multiple power sources. They both harness the power of a diverse range of energy sources, ranging from solar and wind power to hydro and conventional fossil fuel generators.
Both of these innovative solutions enhance the resilience and reliability of the energy supply. They are equipped to diversify the energy sources they use, ensuring a stable supply of electricity even in the event of a power outage or a fluctuation in a specific energy source.
What is a Microgrid
Another shared aim between hybrid energy systems and microgrids is their commitment to localized energy generation. Both technologies have the potential to reduce dependence on central power grids, instead enabling specific communities or areas to generate their own electricity. This model of power generation secures a greater degree of energy security and also reduces potential transmission losses.
In addition, hybrid energy systems and microgrids both contribute significantly to environmental sustainability. They incorporate renewable energy sources into their systems, thereby minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and reducing carbon footprints.
Finally, both systems can offer substantial cost savings and optimize energy efficiency. Hybrid energy systems can flexibly use different energy sources based on their availability and cost-effectiveness, leading to significant reductions in energy expenses. Microgrids follow suit by making efficient use of local energy generation and reducing transmission losses, also leading to cost savings and improved energy efficiency.
While there are noticeable similarities between hybrid energy systems and microgrids, it is important to note that they are not identical. Microgrids tend to focus more on localized energy distribution and management, while hybrid energy systems cover the broader concept of integrating multiple energy sources. Despite their differences, both systems are integral to a future of sustainable and resilient energy solutions.
The way a hybrid energy system operates is largely dependent upon the types of renewable power that it is based on.
For solar-wind hybrids, the system’s wind turbines are often powered by an array of photovoltaic solar panels. These panels provide the turbine with enough energy to keep spinning when wind currents are weak, thereby allowing the turbine to continue generating electricity. In a solar-fuel cell mix, solar panels are used to generate an electric current that can trigger chemical reactions within a fuel cell and produce hydrogen gas, which is then converted into electricity. By combining two or more forms of alternative energy, a completely sustainable and carbon neutral system can be created.
Example of a wind-hydro system…
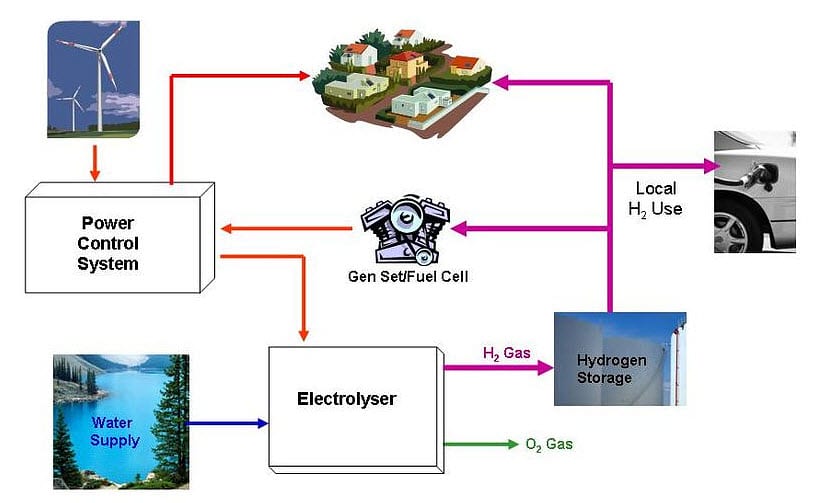
One practical application of a Hybrid Energy System is a power station that utilizes wind turbines, solar panels, and hydrogen fuel cells. The wind turbines and solar panels harness energy from wind and the sun correspondingly, transforming it into power. Electricity created during intervals of strong wind or intense sunlight can be harnessed to generate hydrogen via electrolysis. This stored hydrogen can be used later in fuel cells to create electricity if there’s low wind or sunlight, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply.
In summary, a Hybrid Energy System synergizes multiple energy sources, like wind and solar, with a hydrogen fuel cell system, providing an efficient and eco-friendly solution to power generation. 
Unleash the Power of Hydrogen: The Solution to Long Term Energy Storage
The world of renewable energy has been grappling with the issue of long-term energy storage for some time now. But what if the solution has been right before our eyes, in the most abundant element in the universe?
Hydrogen, the simplest and lightest element, is stepping into the spotlight as a feasible solution for long-standing challenges in renewable energy storage. A recently published document titled “Hydrogen fuel and electricity generation from a new hybrid energy system based on wind and solar energies and alkaline fuel cell” in the journal Energy Reports has shed light on this promising avenue.
Authored by Mohammad Reza Foroughi, Zahra Khakpour, and Amir Maghsoudipour, the document refers to the potential of hydrogen to revolutionize energy storage. The key here lies in hydrogen fuel cells, known for their exceptional ability to store and release energy efficiently.
Although the full text of this research is not readily available, the implications are exciting and full of potential. It’s clear that the answer to renewable energy’s long-term storage problems could be stashed away within hydrogen fuel cells – an option that’s not only efficient but also abundant and accessible.
In conclusion, hybrid energy systems represent a promising step forward in our quest for sustainable and efficient power generation. By harnessing the strengths of multiple renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, and combining them with hydrogen fuel cells, these systems are able to provide a reliable and steady supply of clean energy. Furthermore, their close relation to microgrids highlights the potential for localized energy generation, reducing dependence on centralized power grids and minimizing transmission losses, thereby contributing to environmental sustainability. Although there are differences between the two, both hybrid energy systems and microgrids play a crucial role in the future of resilient energy solutions.
Lastly, the role of hydrogen as a solution to long-term energy storage cannot be underestimated. This abundant element may just hold the key to overcoming one of the biggest challenges in the renewable energy sector. As we continue to explore and innovate, the possibilities for clean, efficient, and sustainable power generation seem increasingly within our grasp.


 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.