Solar energy refers to the harnessing of the radiant light and heat produced by the sun.
It is, perhaps, one of the most ancient forms of clean energy in the world, taking a variety of forms over the years and representing myriad incarnations of technology. These technologies take two forms: Passive and active. Both types of solar technology harness the power of the sun in different ways, but produce similar results in terms of electricity and heat
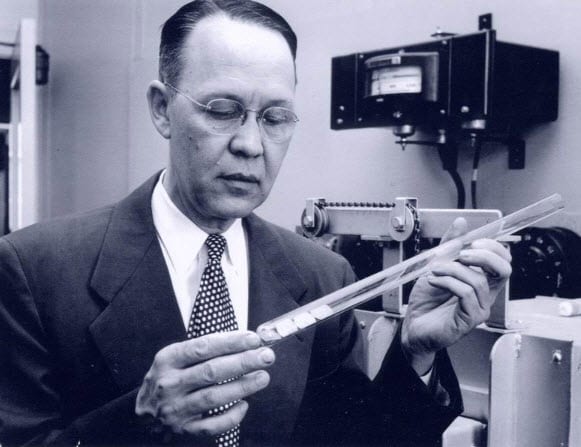
Calvin S. Fuller working on the first solar cell – Image from Wikipedia
The Earth receives approximately 174 petawatts of solar radiation, 30% of which is reflected by into space or absorbed by clouds, oceans, and the planets landmasses. The rest of that solar radiation goes largely untapped. This energy is becoming increasingly valuable to the world, especially to developing countries that are finding traditional forms of energy too costly. Typically, solar energy is harnessed through the use of photovoltaic (PV) panels.
PV solar panels generate electricity by converting solar radiation into a direct current using a myriad of semiconductors.
These semiconductors are the basis of solar technology because they exhibit photovoltaic effects. Traditional solar panels have been used for a variety of applications and are even one of the primary sources of energy for the International Space Station. As technology advances, however, panels are beginning to evolve and become more efficient, making solar energy more attractive to those that had long questioned its viability.
Solar cells, 3D solar systems, and concentrated solar energy farms are examples of how solar technology is evolving.
These technologies are harnessing the power of the sun more effectively and efficiently than traditional PV solar panels. The energy garnered by these technologies can be used for many purposes, such as water treatment and transportation. Solar energy has recently been growing in popularity as a residential energy.
The German and Japanese governments have ambitious feed-in tariffs in place to help support the growth of solar energy amongst homeowners. These plans provide a financial incentive for homeowners to install solar panels and similar solar technologies on their properties. In the case of Germany, those with homes equipped with solar energy systems have the opportunity to sell the clean energy these systems generate back to the government. This plan has proven so successful in Germany, that the government had to make cuts to the subsidies it provides homeowners in late 2011 or risk running out of money.
their properties. In the case of Germany, those with homes equipped with solar energy systems have the opportunity to sell the clean energy these systems generate back to the government. This plan has proven so successful in Germany, that the government had to make cuts to the subsidies it provides homeowners in late 2011 or risk running out of money.
The success of these solar energy feed-in tariffs have cause the advancement of solar technology and the adoption of solar energy to increase dramatically. Similar plans are beginning to crop up all over the world, such as the U.S. and the United Kingdom. Countries near the Earth’s equator that receive a large amount of solar radiation are also seeing a great deal of interest from energy companies who wish to exploit their exposure to the sun. For these countries, this interest represents promising economic growth.
Other Images and Material About Solar Power:

Solar Powered Flight 2001
First Solar Powered Home in 1939

Solar Plant in San Bernardino CA



 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.