
H2SITE Expands Hydrogen Production via Ammonia Cracking in Norway
January 23, 2026You can tell H2SITE means business: they’ve just set up H2SITE Norway AS in Bergen. This move marks their jump from R&D to commercial rollout, aiming to deploy on-board ammonia-to-hydrogen cracking systems for vessel propulsion and auxiliary power, tapping into Norway’s deep maritime expertise, ambitious industrial decarbonization goals and growing hydrogen production networks.
Back in Bilbao, this Spanish upstart has already racked up over 6,000 hours running their cutting-edge membrane reactor technology since 2023. At their Loiu (Bizkaia) plant, they’re cranking out thousands of palladium-alloy membranes every year. Thanks to a fresh €36 million injection, they’re ready to leap from pilot tests to early commercial projects.
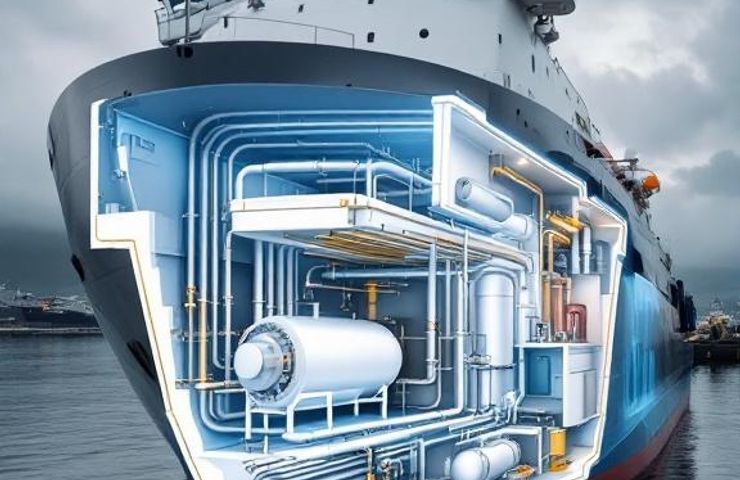
Ammonia Cracking: Inside the System
The magic happens inside a neat, compact membrane reactor that does both decomposition and separation in one go. You feed it clean ammonia, and under a catalyst it breaks apart to free up hydrogen. The palladium-alloy membranes then act like VIP bouncers, letting only fuel-cell-grade hydrogen slip through while keeping nitrogen and any leftover ammonia out. The endgame? A steady stream of high-purity hydrogen or a custom blend that marine engines can handle with ease.
And they’re not stopping at benchtop demos. H2SITE is scaling up to megawatt-class units built to slide right into a ship’s energy module. That means vessels can whip up enough onboard hydrogen to power electric drives or auxiliary generators—no shore-side stops needed. It’s a big leap for beefing up hydrogen infrastructure on the water.
Strategic Footprint in Norway
Norway’s robust shipping scene is a natural proving ground. With strict emissions rules and a pragmatic stance on first-of-a-kind tech, they’re already kicking the tires on ammonia as a marine fuel carrier. Bergen, with its network of shipyards and technology partners, gives H2SITE Norway AS the perfect sandbox to weave these systems straight into new vessel designs.
The subsidiary will be out there, rubbing shoulders with shipowners, yards and fuel suppliers, gathering real-world data to fine-tune performance and nail down operational protocols in some of the toughest maritime conditions you can imagine.
Implications for Maritime Decarbonization
Building on pilots like H2Ocean and APOLO, H2SITE’s Norway move really shows off ammonia’s chops as a zero-carbon carrier. Generating hydrogen on demand means you can ditch those bulky compressed-gas tanks and messy logistics. For early adopters, that could translate into a lower total cost of ownership—no more fretting over methane slip and a straight shot at hitting the IMO’s carbon intensity targets. It’s a big win for clean ammonia and zero-emission technology.
Of course, it’s not all smooth sailing. Regulations around ammonia bunkering and onboard safety protocols are still catching up. Shipowners will have to weigh operational risks against the ticking clock of tightening EU and IMO rules.
If H2SITE gets it right in Norway, they’ll walk away with a blueprint for the rest of the globe. Fine-tuning those membrane reactors in live demos could pave the way for everything from short-sea hops to transoceanic voyages—solidifying ammonia cracking as a pillar of zero-emission technology.

 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.