JERA Secures METI Certification for Low-Carbon Ammonia Supply Chain
January 5, 2026This last December Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) stamped JERA Co., Inc. as a certified supplier of low-carbon hydrogen and its derivatives. Thanks to this endorsement under the Hydrogen Society Promotion Act’s Price Gap Support Scheme, JERA can now tap government subsidies to import 492,144 mt/y of clean ammonia from Louisiana’s Blue Point project. This move is a game-changer for blending ammonia with coal at Hekinan Thermal Power Station and marks a major milestone in Japan’s first full ammonia value chain and wider sustainable energy push by FY2029.
Bridging the Price Gap with Subsidies
The Price Gap Support Scheme kicked off in October 2024 to help close the cost gap between low-carbon fuels and their conventional counterparts. METI has set aside a whopping ¥3 trillion over 15 years, covering the difference between a reference price for grey hydrogen/ammonia and actual import or production costs—so long as you lock in supply contracts for at least a decade. For JERA, that reliability translates into solid cash flow, making its Louisiana-sourced ammonia a competitive alternative to coal and LNG.
From Louisiana’s Blue Point to Japan’s Coal Fleet
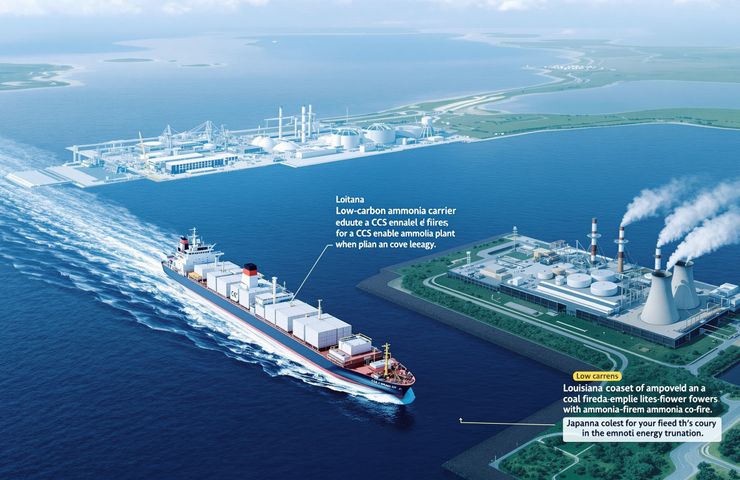
In April 2025, JERA joined forces with CF Industries (40% stake) and Mitsui & Co. (20%) to give the green light to the Blue Point low-carbon ammonia plant in Ascension Parish, Louisiana. The facility will crank out 1.4 million mt/y of ammonia using steam methane reforming paired with CCS that captures over 95% of CO₂ emissions. JERA holds a 35% share and offtake rights to roughly one-third of the output.
Starting in 2030, JERA plans to ship around 492,144 mt/y of this ammonia—enough to replace 20% of the heat value in one 1 GW unit at Hekinan—by chartering four specialized carriers from NYK and MOL subsidiaries. Meanwhile, industrial players in the Chubu region, including Toyota Industries, AGC and NGK Insulators, will tap into this supply to decarbonize their manufacturing processes and hit their industrial decarbonization targets.
Technology Spotlight: Low-Carbon Ammonia & Co-Firing
At Blue Point, hydrogen production kicks off with steam methane reforming, then CCS swoops in to seize over 95% of the CO₂ before it ever paints the atmosphere. That captured hydrogen combines with nitrogen to fuel ammonia production in a low-carbon way. By leveraging existing infrastructure, this method drastically cuts lifecycle emissions compared to old-school plants.
On the ground at Hekinan, they’ve been trialing a 20% heat-value blend of clean ammonia with coal since 2024. By FY2029, the goal is to roll this blend out across major coal units, shaving up to 20% of CO₂ emissions per megawatt-hour. Operators simply retrofit burners and tweak combustion controls—a handful of proven tweaks from last year’s demo runs.
Strategic Implications & Risks
This METI certification is more than just a rubber stamp—it cements JERA’s leadership in industrial decarbonization. Under its JERA Zero CO₂ Emissions 2050 initiative, the company’s pledged to hit net-zero by mid-century. Locking in those subsidies takes the edge off capital risks for the Blue Point project and guarantees long-term supply for power generators and manufacturers.
That said, the model leans heavily on steady government support and top-notch CCS performance. If subsidy rules get shuffled or capture rates fall short, costs could climb. Still, this pioneering chain—from U.S. sustainable energy production to maritime logistics to Japanese co-firing—serves as a solid blueprint for other markets ramping up climate-friendly fuel solutions.
Forward Look: What’s Next?
As JERA preps for its inaugural shipments in 2030, stakeholders will be watching CCS efficiency at Blue Point, the seamless operation of ammonia carriers, and Hekinan’s full-scale co-firing ramp-up. Just around the corner, Mitsui’s own 280,000 mt/y certified ammonia venture slated for 2031 and Japan’s broader hydrogen infrastructure rollout will provide handy benchmarks. If everything clicks, this end-to-end supply chain could spur similar deals across Europe and Asia.
About JERA Co., Inc.
JERA is Japan’s largest power generation company, formed in 2015 from a TEPCO Fuel & Power and Chubu Electric Power joint venture. Based in Tokyo, JERA’s portfolio spans coal, LNG, renewables, and trailblazing ammonia co-firing and hydrogen initiatives—all part of its drive to achieve net-zero CO₂ by 2050.


 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.