
The Clock is Ticking: Can the Auto Industry Meet the 2030 Zero Emission Targets?
October 28, 2024 0 By John MaxA recent report from MorningStar highlights the critical role the transportation sector plays in global energy-related carbon dioxide emissions, contributing over 20% to the total. As the world faces the pressing need to tackle climate change, the path to achieving net zero emissions by 2050, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, relies heavily on the rapid expansion of zero emission car sales. Despite optimistic projections, the report underscores that the journey towards widespread adoption is laden with significant challenges, which could potentially hinder global net zero ambitions.
EV Sales Forecasts: Can We Hit the Mark?
Under the Inevitable Policy Response (IPR) scenario, zero emission car sales are expected to constitute more than 80% of total car sales by 2030. This transition is deemed essential for limiting global warming to well below two degrees Celsius. However, as of 2023, electrified vehicles only accounted for about 16% of global car sales. The slowing growth in demand poses a significant threat to these targets, risking delays in global efforts to curb carbon emissions.
Implications for Net Zero Ambitions
The deceleration in EV sales growth poses a significant challenge to achieving net zero targets, as the swift adoption of EVs is critical for reducing emissions in line with international climate agreements. However, amidst these growing pains, hydrogen cars present a promising alternative. With their ability to refuel quickly and deliver longer ranges, hydrogen vehicles could excel where EVs struggle, offering a viable solution to help countries meet their emissions commitments. As technological breakthroughs and infrastructure investments advance, hydrogen cars can complement EVs in the quest for a sustainable transportation future, providing the much-needed impetus to bridge the gap towards net zero objectives.
Auto Manufacturers’ Concerns
In Europe, auto manufacturers face mounting pressure from looming stricter EU emissions targets set to take effect in 2025. Many automakers, having banked on robust EV sales growth to meet these standards, are now lobbying for relief measures due to the recent slowdown. This situation underscores the precarious balance between regulatory demands and market realities.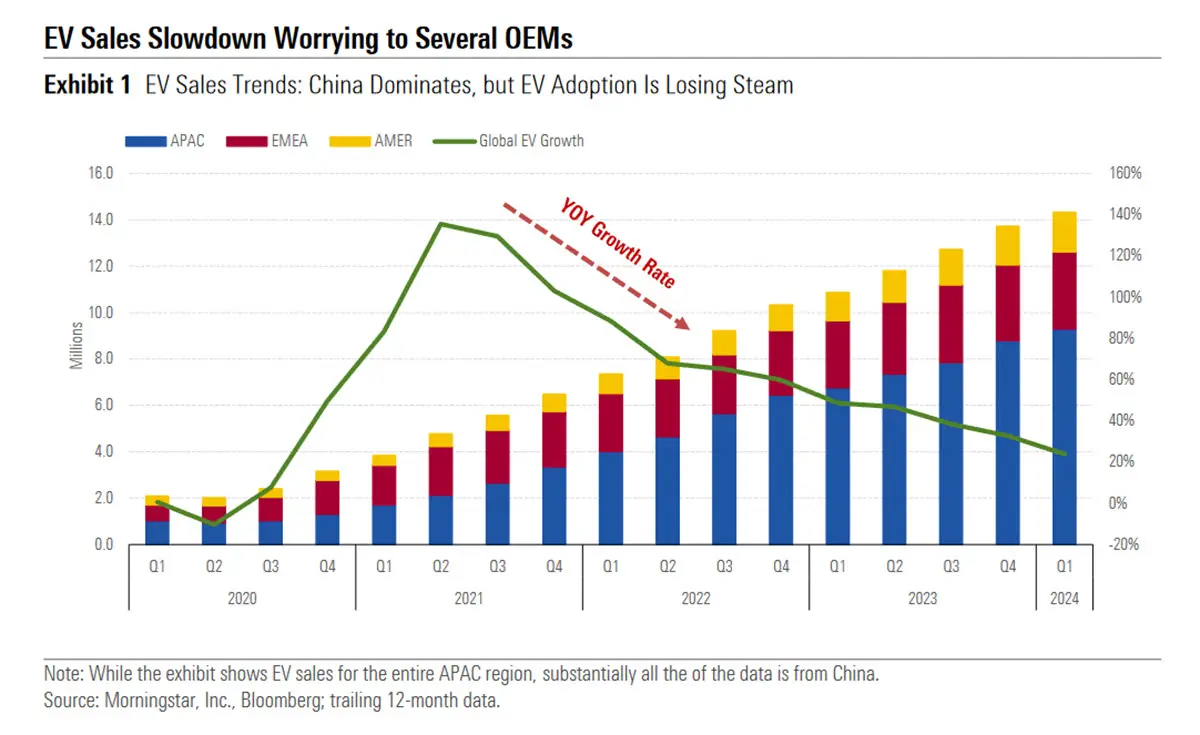
State of the Auto Manufacturing Industry
-
Volkswagen AG’s Situation:
- VW is contemplating potential plant closures in Germany after weak financial results in H1 2024 and issuing a profit warning.
- The brand’s operating margin dropped to 2.3%, far below its 2026 target of 6.5%.
- Cost reduction strategies, including early retirement and redundancy, have proven inadequate, with stronger measures under consideration.
- VW is losing EV market share in Europe to emerging Chinese automotive OEMs.
-
Broader Automotive Industry Trends:
- Many OEMs are reassessing their EV strategies due to lackluster demand.
- Earnings potential is constrained by slowing demand, lower pricing, and persistent cost challenges.
- Legacy OEMs rely on ICE vehicle sales to support their EV transition and new mobility ventures.
- The Chinese market presents additional challenges due to its size and earnings impact.
-
Ford Motor Company’s Reaction:
- Ford cancelled plans for three-row all-electric SUVs as it updates its electrification strategy.
- The company reported significant losses in its EV segment, Ford Model e, totaling $4.7 billion in 2023 and $2.5 billion in H1 2024.
-
General Motors Company’s Adjustments:
- GM lowered its 2024 EV production target and delayed the launch of its first Buick EV model.
- It withdrew its target of 1 million EV units annually by the end of 2025.
-
Mercedes-Benz Group AG’s Strategy:
Challenges in the EV Market
Despite technological advancements, EVs continue to face significant hurdles, including range anxiety and charging infrastructure issues. Extreme weather can reduce EV range by about 25%, and charging stations suffer from reliability problems. Additionally, high repair costs and insurance premiums remain deterrents.
Chinese OEM Influence
Chinese manufacturers, like BYD Company, dominate the affordable EV market, supported by government incentives. With a NEV penetration rate of 32.4% in early 2024, China aims for 45% by 2027. This growth challenges legacy automakers and has prompted tariffs from the EU and U.S., forcing Chinese OEMs to consider production relocation.
Conclusion: Navigating Growing Pains and the Hydrogen Alternative
To overcome these challenges, the auto industry must innovate and adapt. Solutions may include improved battery technology, expanded charging infrastructure, and strategic partnerships. The hydrogen car market faces similar growing pains, such as high costs and infrastructure needs. However, it offers an alternative path that could complement EV efforts, providing another avenue to achieve net zero goals. As the global push for sustainable transportation intensifies, both EVs and hydrogen cars will play crucial roles in shaping a cleaner future.
About The Author
John Max is an experienced sound engineer with a bachelor’s degree from UCLA. With over 25 years of experience in the entertainment industry, John has also worked as a machinist, producing parts for cameras. Apart from his professional achievements, John is passionate about classic cars, owning a dazzling 1976 Porsche 911. While he drives a Toyota Prius on a regular day, John is excited about getting his hands on his first hydrogen car soon. John has been an avid writer for Hydrogen Fuel News for 17 years, contributing to the team as they collectively investigate and learn about the growth and technology of hydrogen fuel. At Hydrogen Fuel News, John is part of a great team that shares a common goal of exploring and investigating the world of hydrogen fuel.




 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.