Study highlights bright future for solid oxide fuel cells
December 18, 2013Global market for fuel cells shows strong growth
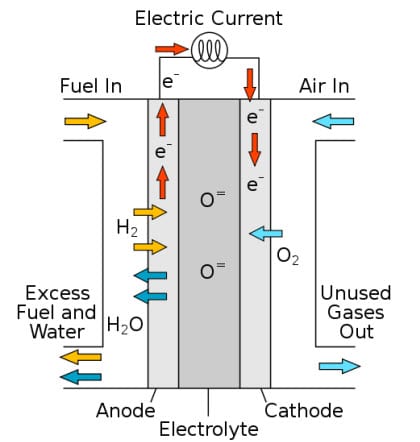 Wintergeen Research has published a new study concerning the global market for solid oxide fuel cells. These fuel cells have seen significant use in several industries over the past several years. As stationary energy units, they are designed to produce more electrical power than their portable counterparts. These fuel cells also produce a significant amount of heat, which can be used for a variety of purposes. Beyond industry, solid oxide fuel cells have also begun to make progress in the residential sector, adding further value to these energy systems.
Wintergeen Research has published a new study concerning the global market for solid oxide fuel cells. These fuel cells have seen significant use in several industries over the past several years. As stationary energy units, they are designed to produce more electrical power than their portable counterparts. These fuel cells also produce a significant amount of heat, which can be used for a variety of purposes. Beyond industry, solid oxide fuel cells have also begun to make progress in the residential sector, adding further value to these energy systems.
Stationary fuel cell market to reach $9.6 billion by 2019
The study highlights the growing interest that has come to surround solid oxide fuel cells. According to the study, the global market for these particular fuel cells will reach $9.6 billion by 2019. Emerging markets around the world will play a relatively small role in the growth of these fuel cells, but well established markets, like those in North America and Europe.
Study highlights methanol fuel cells as well
The study also shows that methanol fuel cells are beginning to gain more attention. These fuel cells rely on methanol to produce electrical power rather than hydrogen. Methanol fuel cells have gained popularity in waste-to-electricity initiatives, where landfills are tapped as a source of methanol production. These types of fuel cells can effectively serve as waste management systems by capitalizing on the gases produced by landfills and using these gases to generate electrical power.
Cost of fuel cells may deter growth
Fuel cells of all kinds are still faced with significant problems that could impede their adoption in the future. One of the most significant of these challenges has to do with cost. Solid oxide fuel cells are somewhat more expensive than other kinds of fuel cell systems due to their size and their use of expensive materials. If the costs associated with fuel cell adoption cannot be reduced, the progress that these energy systems are expected to see in the coming years may diminish.


 With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.
With over 15 years of reporting hydrogen news, we are your premier source for the latest updates and insights in hydrogen and renewable energy.